- Root is the super user its has the ability to do anytask on a system. To protection against potential damage sudo is used in place of root.
- Sudo allows users and groups access to commands they normally would not be able to use.
- Sudo will allow a user to have administration privileges without logging in as root. A example of the sudo command is as follows:
Saturday, May 20, 2017
Understanding Sudo
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
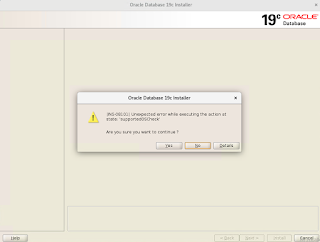
Oracle Database 19c Installation on Oracle Linux 7
Pre-installation settings before installing Oracle Database 19c SELinux If the OS is to be used for an Oracle installation, it is ...
-
Method 1 : To turn on the option for storing chat history: Open Skype for Business/Lync and sign in. Click Show Menu arrow nex...
-
Start the installation setup. Click Next. Accept the license and Click Next. Enter the User Name and Organisation. Check the installation fo...
-
How to Extract .zip File: This is the most common compression format used by various IT professions on many operating systems. For this you ...

No comments:
Post a Comment